Insulin's Role in Blood Sugar
In the world of diabetes management, understanding the function of insulin is key to taking charge of your health. Did you know that a well-balanced level of insulin can be the difference between energy and fatigue? Here’s what you will learn about this essential hormone and its role in blood sugar regulation.
What You Will Learn
- Insulin's Function: Insulin helps cells absorb glucose, lowering blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Interaction: Glucagon works opposite to insulin by raising blood sugar levels when needed.
- Types of Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes involves insulin deficiency, while Type 2 is often characterized by insulin resistance.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of blood sugar levels is essential to adjust insulin therapy effectively.
The Insulin-Glucagon Balance in Glucose Regulation
This visual illustrates the cyclical relationship between Insulin and Glucagon, two key hormones that maintain glucose homeostasis.
The Connection Between Insulin and Blood Sugar Regulation
Understanding how insulin impacts blood sugar regulation is crucial for anyone managing diabetes. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a vital role in maintaining glucose homeostasis—the balance of glucose levels in the bloodstream. In simple terms, when we eat, our bodies convert food into glucose, which is essential for energy. Insulin helps transport this glucose into our cells, and it works in tandem with another hormone called glucagon to ensure our blood sugar levels remain stable.
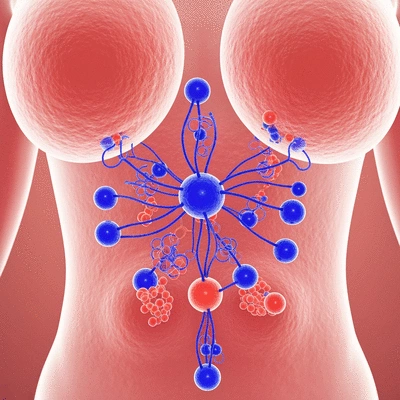
Without adequate insulin, blood sugar levels can rise dangerously high, leading to various health complications. This interplay between insulin and glucagon is fundamental to our understanding of diabetes, demonstrating why it’s critical to maintain a delicate balance.
Understanding Insulin's Role in Glucose Homeostasis
Insulin acts as a key that unlocks the door to our cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy. When we consume carbohydrates, our blood glucose levels increase, triggering the pancreas to release insulin. This process not only decreases blood sugar but also signals the liver to stop producing glucose, creating a harmonious balance in our body’s energy supply. For more detailed insights into how eating and fasting regulate insulin, you can refer to research from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK).
- Insulin Release: Triggered by rising blood sugar levels post-meal.
- Glucose Uptake: Insulin facilitates the entry of glucose into muscle and fat cells.
- Glucagon's Role: Works inversely to insulin by raising blood sugar levels when they drop too low.
This cyclical relationship between insulin and glucagon highlights how our bodies work together to manage energy levels effectively. A deeper understanding of this process can empower individuals to make informed choices in their diabetes management journey.
The Physiological Mechanisms of Insulin Action
Insulin’s primary function is to promote glucose uptake in muscle and fat tissues. When insulin is released, it binds to insulin receptors on cell surfaces, initiating a cascade of events that allows glucose to be absorbed. This action not only fuels our cells but also plays a critical role in metabolism and overall health. You can explore further information on insulin's physiological mechanisms in this article on insulin receptors.
As someone passionate about educating others on diabetes, I often emphasize that enhancing our understanding of these physiological mechanisms can lead to better management practices. Knowing how insulin works can help individuals make smarter lifestyle choices that support their health.
Insulin Secretion: How the Pancreas Responds to Blood Sugar Levels
At the heart of insulin production are the pancreatic beta cells. These specialized cells are crucial in sensing blood sugar levels and adjusting insulin secretion accordingly. When blood sugar rises, beta cells spring into action, releasing insulin to keep levels in check. Conversely, when blood sugar drops, insulin secretion decreases.
This finely tuned process is essential for maintaining normal blood sugar levels. When the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin or when the body becomes resistant to its effects, complications can arise, leading to diabetes. Understanding this mechanism is vital in recognizing the importance of insulin in our overall health. Learn more about the complex dynamics of insulin secretion and its regulation through scientific research.
The Impact of Insulin on Glycogen Storage
Another significant role of insulin is its ability to facilitate glycogen synthesis in the liver and muscle tissues. When we consume carbohydrates, insulin triggers the conversion of excess glucose into glycogen, which is stored for later use. This storage form of glucose acts as a reservoir of energy, readily available when our body needs it, especially during periods of fasting or intense exercise.
- Glycogen Storage in the Liver: Supports blood sugar balance during fasting.
- Muscle Glycogen: Provides quick energy during physical activity.
- Insulin Deficiency: Leads to diminished glycogen stores and increased blood sugar levels.
By understanding how insulin influences glycogen storage, individuals can appreciate the importance of maintaining stable insulin levels and the impact of dietary choices on their health.
Pro Tip
To enhance your understanding of insulin and its effects on blood sugar levels, consider keeping a daily log of your meals and corresponding blood sugar readings. This practice can help you identify how different foods impact your glucose levels and enable you to make more informed dietary choices.
Summarizing the Importance of Insulin in Diabetes Management
Understanding insulin's role in diabetes management is crucial for anyone living with this condition. It acts as a key player in maintaining blood sugar regulation and works in conjunction with other hormones, such as glucagon. Together, they help keep our glucose levels stable, enabling us to function at our best!
In summary, insulin is essential for promoting the uptake of glucose into our cells, which provides energy for daily activities. Without effective insulin action, managing diabetes becomes significantly more challenging.
Key Takeaways on Insulin and Blood Sugar Regulation
Here are some key points to keep in mind about insulin and its role in diabetes management:
- Insulin's Function: Insulin helps cells absorb glucose, lowering blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Interaction: Glucagon works opposite to insulin by raising blood sugar levels when needed.
- Types of Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes involves insulin deficiency, while Type 2 is often characterized by insulin resistance.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of blood sugar levels is essential to adjust insulin therapy effectively.
These points highlight just how vital insulin is in keeping our blood sugar levels balanced. The interplay between insulin and other hormones is a delicate dance that requires attention and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions About Insulin and Blood Sugar Regulation
- Q: What is insulin and what is its main function?
- A: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. Its main function is to help cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, thereby lowering blood sugar levels and providing energy.
- Q: How does glucagon relate to insulin?
- A: Glucagon works in opposition to insulin. When blood sugar levels drop too low, glucagon is released by the pancreas to signal the liver to release stored glucose, thus raising blood sugar levels.
- Q: What is glucose homeostasis?
- A: Glucose homeostasis refers to the body's process of maintaining stable blood glucose levels. This balance is primarily achieved through the coordinated actions of insulin and glucagon.
- Q: How does insulin affect glycogen storage?
- A: Insulin facilitates glycogen synthesis, which is the process of converting excess glucose into glycogen for storage in the liver and muscle tissues. This stored glycogen serves as an energy reserve.
- Q: Why is regular monitoring of blood sugar levels important?
- A: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes to understand how their body responds to food, exercise, and medication, allowing for effective adjustment of insulin therapy and lifestyle choices.
Empowering Patients through Knowledge and Action
As someone who cares deeply about diabetes management, I encourage you to take charge of your health through knowledge and action. By understanding how insulin works, you can make informed decisions about your lifestyle and treatment options.
Working closely with healthcare providers is also essential. They can help tailor a management plan that meets your unique needs. Here are some steps you can take:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about insulin, its functions, and how it affects your body.
- Engage in Active Management: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels and adjust your diet and exercise accordingly.
- Build a Support System: Connect with healthcare professionals, family, and support groups for motivation and advice.
By implementing these strategies, you can empower yourself to manage diabetes effectively. Remember, informed patients lead to healthier lives, and at What Is Diabetes, we’re here to support you every step of the way!
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Insulin's Function: Insulin helps cells absorb glucose, lowering blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Interaction: Glucagon works opposite to insulin by raising blood sugar levels when needed.
- Types of Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes involves insulin deficiency, while Type 2 is often characterized by insulin resistance.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of blood sugar levels is essential to adjust insulin therapy effectively.
- Glycogen Storage: Insulin facilitates the conversion of excess glucose into glycogen for energy storage.









