Type 1 vs Type 2 Diabetes
Understanding diabetes can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. As you embark on this journey of self-education, consider how informed choices can lead to a healthier life.
What You Will Learn
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition requiring lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 diabetes stems from insulin resistance and can often be managed through lifestyle changes.
- Common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, and extreme fatigue.
- Understanding the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is crucial for effective management.
- Connecting with diabetes support groups can provide valuable emotional support and practical advice.
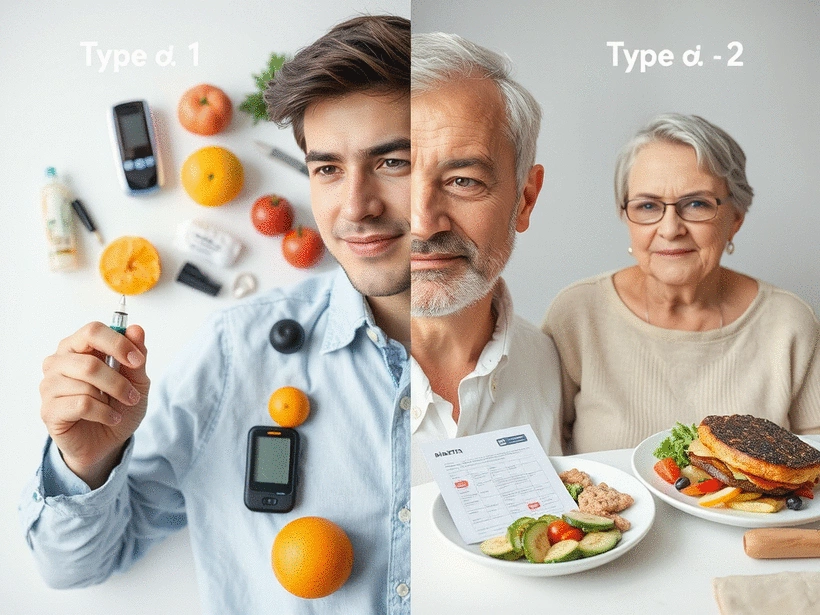
Type 1 vs. Type 2 Diabetes: A Quick Comparison
This visual highlights the key distinctions between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes regarding their causes, onset, and management approaches.
Type 1 Diabetes
- • Cause: Autoimmune condition
- • Onset: Childhood or adolescence
- • Management: Requires insulin therapy
- • Symptoms: Develop suddenly
Type 2 Diabetes
- • Cause: Insulin resistance
- • Onset: Usually in adults
- • Management: Lifestyle changes, oral meds
- • Symptoms: Develop gradually
Understanding Diabetes: Key Definitions and Overview
Understanding diabetes can indeed feel overwhelming, but it’s crucial to grasp the basics for effective management. At What Is Diabetes, we believe that informed patients can lead healthier lives. Let’s explore the key definitions surrounding this condition to shed light on what diabetes really is!
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This leads to little or no insulin production, which is essential for converting glucose into energy. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes typically require insulin therapy from the time of diagnosis to manage their blood sugar levels.
- Commonly diagnosed in children or young adults
- Symptoms can develop suddenly
- Requires lifelong management with insulin
Recognizing these aspects is vital, as Type 1 diabetes management is fundamentally different from Type 2 diabetes, which we’ll dive into next.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?

In contrast, Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body either does not use insulin effectively or does not produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. This type is often associated with lifestyle factors and can develop at any age, although it is more prevalent in adults. Managing Type 2 diabetes typically involves lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise.
- More common in adults, though rising in younger populations
- Symptoms develop gradually
- Management may include oral medications in addition to lifestyle changes
Understanding the differences between these two types helps lay the foundation for effective diabetes management strategies!
Common Symptoms of Diabetes: Recognizing the Signs
Regardless of the type, recognizing common symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Some of the most frequent signs include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Extreme fatigue and irritability
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained weight loss or weight gain
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early awareness can significantly impact your diabetes management journey.
Pro Tip
Did you know? Regular monitoring of your blood sugar levels can significantly enhance your diabetes management. Keeping a log of your readings helps you identify patterns and make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and medication. Consider using a mobile app to simplify tracking and analysis!
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetes
- What is the main difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells, leading to no insulin production. Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body doesn't use insulin effectively or produce enough.
- What are the typical age groups for diagnosis of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
- Type 1 diabetes is commonly diagnosed in children or young adults, while Type 2 diabetes usually develops in adults, though it is increasingly seen in younger populations.
- How is Type 1 diabetes managed?
- Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy from the time of diagnosis.
- How is Type 2 diabetes typically managed?
- Type 2 diabetes often involves lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise, and may also include oral medications.
- What are common symptoms of diabetes?
- Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, blurred vision, unexplained weight changes, and slow-healing sores or frequent infections.
Recap of Main Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes

Understanding the distinctions between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes can be crucial for effective management and treatment. As someone who has been in the field for over a decade, I’ve seen firsthand how these two types can impact individuals differently. Here’s a quick recap of the main differences to help you better navigate your diabetes journey!
Summarizing Key Points: A Quick Reference Guide
- Causes: Type 1 diabetes is primarily an autoimmune condition, while Type 2 diabetes is linked to insulin resistance.
- Onset: Type 1 typically appears in childhood or adolescence, whereas Type 2 usually develops in adults.
- Management: Type 1 requires insulin therapy from day one, while Type 2 can often be managed through lifestyle changes.
- Symptoms: Both types share symptoms like increased thirst and frequent urination, but Type 1 symptoms can develop rapidly.
- Risk factors: Family history plays a significant role in both types but is particularly notable in Type 2 diabetes.
These points serve as a concise reference for differentiating between the two diabetes types. Remember, being informed empowers you to make better health choices! For more detailed insights on each type, head back to the earlier sections of our guide.
Next Steps: Taking Charge of Your Health
Now that you have a clearer understanding of the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, let’s look at how you can take charge of your health moving forward. Managing diabetes is a lifelong journey, and having the right resources is essential for success!
Resources for Further Information and Support, Including Diabetes Support Groups
- Diabetes Support Groups: Connecting with others can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Educational Websites: Platforms like What Is Diabetes offer valuable information and tips for managing your condition.
- Local Community Events: Look for health fairs or workshops in your area that focus on diabetes management.
Utilizing these resources can help you stay informed and empowered. Engaging with community support can also make a significant difference in your management journey.
Encouragement to Seek Professional Guidance from Endocrinologists and Health Educators
I encourage you to consult with healthcare professionals—especially endocrinologists and certified health educators—who can guide you in tailoring a management plan that fits your unique needs. They can provide personalized insights, adjust your treatment as necessary, and help you stay on track with your health goals.
Remember, taking proactive steps today can lead to a healthier tomorrow! So, what’s the first step you’ll take towards managing your diabetes?
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition requiring lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Often linked to lifestyle factors, managed through diet, exercise, and sometimes medications.
- Common Symptoms: Increased thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores are signs to watch for.
- Management Strategies: Early diagnosis and professional guidance are crucial for effective management.
- Resources: Engage with diabetes support groups and educational websites for ongoing support and information.









